HEMOPHILIA - (also Haemophilia)
A genetic Blood disorder that causes the Blood unable to form a firm clot normally and quickly. Frequent bleedings into the joints following minor trauma causes severe pain, swelling and disability.
HEMOCHROMATOSIS
A most often hereditary Blood disorder that causes body tissue to absorb and store too much iron. Hemochromatosis is not "caught." The disease (which is actually many diseases) has also been known to develop in spite of dietary iron intake in normal quantity
LEUKEMIA
Often referred to as cancer of the Blood, a malignant condition affecting the immature Blood-forming cells in the bone marrow. Usual signs are bleeding, anemia and infections
THALASSEMIA
A group of fatal genetic Blood disorders. The WHO recognizes Thalassemia as the most prevalent inherited genetic Blood disorder in the world. It is more prevalent in north India.
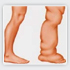
LYMPHATIC FILARIASIS
Lymphatic filariasis is a debilitating disease caused by nematode worms of the genera Wucheriaand Brugia. Larval worms circulate in the Blood stream of infected persons, and adult worms live in the lymphatic vessels.
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE
The most common risk factor for heart and kidney diseases and stroke. High Blood Pressure, or Hypertension, is defined in an adult as a systolic pressure (top number) of 140 mm Hg or higher and/or a diastolic pressure (bottom number) of 90 mm Hg or higher. Blood pressure is measured and noted in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
SICKLE CELL DISEASE
A hereditary Blood disease resulting from a single amino acid mutation of the Red Blood Cells. A Blood condition of anemia. People with sickle cell disease have Red Blood Cells that contain mostly hemoglobin S, an abnormal type of hemoglobin.